Already impressed with the kiwi’s long snoz? Our national icon is also the only bird in the world with external nostrils at the tip of its long beak.
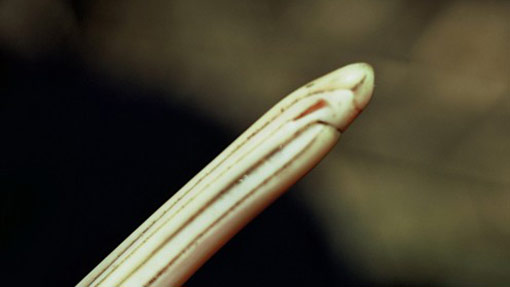
Sense of smell
While the kiwi’s eyesight isn’t great, the parts of it brain devoted to smell and touch are enormous.
A kiwi’s olfactory bulb is the second largest among all birds relative to the size of its forebrain, giving it an exceptional sense of smell, just second to the condor. This helps kiwi locate food beneath the soil and in leaf litter.
Good vibrations
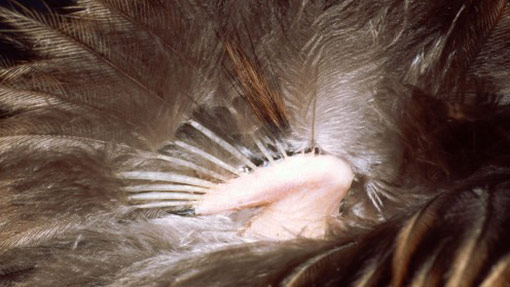
More recently, research has discovered that the kiwi’s beak does much more than smell very well. Massey University PhD student Susan Cunningham found that kiwi have sensory pits at the tip of their beaks which allow them to sense prey moving underground. In fact, the research suggests that feeling the prey’s vibrations may be more important to a hungry kiwi than smelling it. Instead, smell may be mainly used to explore their environment.
The finding surprised researchers. Other probe-feeding birds, such as godwits and sandpipers, also have remarkably sensitive bill-tip organs to pick up prey vibrations, but these shorebirds are only very distant relatives of kiwi. It may be an evolutionary example of two distantly related animals independently coming up with the same solution to the same problem.
A probe & a lever
As it walks, the kiwi taps the ground with its beak, probing the soil and sniffing loudly. It can locate an earthworm up to three centimetres underground. Once a snack has been located, the kiwi pushes its beak deep into the earth. To protect the opening, the tip of the upper beak overlaps the lower one.
The kiwi can use its beak as a lever, moving it back and forth to widen the hole. Sometimes it uses its entire weight to drive the beak deeper, kicking its legs up in a kind of headstand.
Once it has hold of the delicate worm, the kiwi moves very carefully because worms break easily. Sometimes a steady pull will do the job.
Sometimes the kiwi remains motionless until the worm relaxes its grip on its tunnel, and then it gives another tug.
The drawbacks
Having nostrils at the end of its beak helps the kiwi make the best use of its ground-based habitat and gives it an advantage over other birds. But this hunting strategy has drawbacks. Kiwi can often be heard snuffling and snorting loudly to clear dirt from their nostrils.
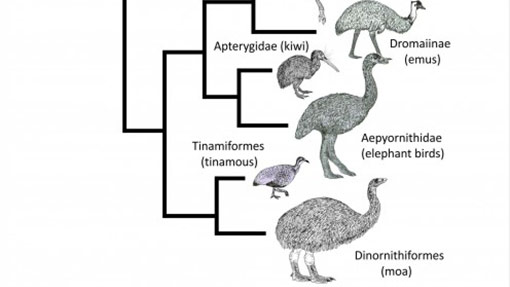
Part of the ratite whānau
Kiwi are part of a group of largely flightless birds known as ratites. Ostriches, emu, and the extinct moa are also part of this group.
Honorary mammals
The kiwi is sometimes referred to as an honorary mammal because of its un-birdlike habits and physical characteristics.
The hidden bird of Tāne
In Māori tradition, all living things on Earth originate from the union of Rangi-nui (the Sky Father) and Papatūānuku (the Earth Mother).
Flightless ... but has wings
The kiwi is one of New Zealand's many flightless birds. They didn't need to fly because there weren't any land mammal predators before man arrived to New Zealand 1000 years ago.
Feathers like hair
Because kiwi do not fly, their feathers have evolved into a unique texture to suit a ground-based lifestyle.
An unusual beak
The kiwi has an extremely unusual beak. Not only does it provide a keen sense of smell, it also has sensory pits at the tip which allow the kiwi to sense prey moving underground.
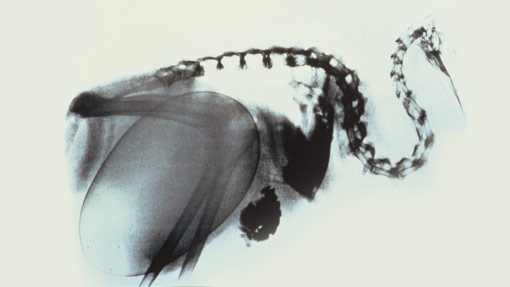
Enormous egg
In proportion to its body size, the female kiwi lays a bigger egg than almost any other bird. While a full term human baby is 5% of its mother's body weight, the kiwi egg takes up 20% of the mother's body.
Kiwi life cycle
Kiwi make their home in many different environments and have been described as 'breeding machines'. With the eradication of predators, the kiwi could be successful once again.
Kiwi signs
Being nocturnal, kiwi can be quite elusive but they do leave signs as to where they have been.
Bird of the night
Kiwi are nocturnal. Like many other New Zealand native animals, they are most active in the dark.
Kiwi calls
Kiwi call at night to mark their territory and stay in touch with their mate. The best time to listen for kiwi is on a moonless night, up to two hours after dark, and just before dawn.
What kiwi eat
Kiwi are omnivores. Their gizzards usually contain grit and small stones which help in the digestion process.
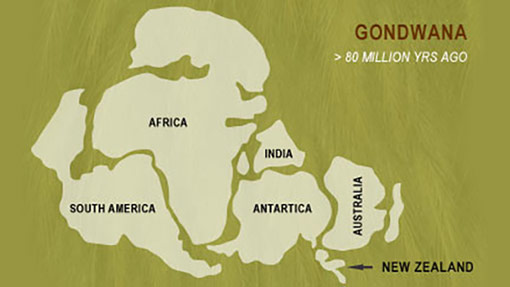
How kiwi came to Aotearoa
Just how did the kiwi journey to New Zealand? Three very different theories have been put forward to explain the mystery.
How kiwi evolved
It is thought that today’s kiwi evolved from one kiwi ancestor that lived about 50 million years ago: a proto-kiwi.
Kiwi myths
Kiwi experts are keen to dispel myths surrounding the kiwi - and there are quite a few!
Learn more about kiwi
Kiwi species
All kiwi are the same, right? Wrong. There are actually five different species of kiwi, all with their own unique features.
Threats to kiwi
The national kiwi population is under attack from many different threats, including predators, loss of habitat, and fragmentation of species.
Where to see kiwi
Many facilities around New Zealand are home to kiwi, plus there are places where, if you're lucky, you could see one in the wild too.
How you can help
Many hands make light work. Keen to join the mission to save the kiwi? Here are some ways you can help.
Protect kiwi
For kiwi to thrive, we all need to work together. Find out what you can do to help save the kiwi, wherever in Aotearoa you happen to be.
Fundraise
To continuing saving the kiwi, conservation groups need funding. Support the mission by making a donation, setting up a fundraising project, or engaging with other fundraising initiatives.
Shop for kiwi
Show your support for Save the Kiwi and some of our wonderful sponsors by purchasing products that will help us do more of what we do.
Donate
Make a quick donation, donate a day of annual leave or invest to save the kiwi.